Lab 5 Reference Document
Part 1: .vimrc addendum and ssh config
In the file ~/.vimrc on ieng6, add:
set cindent
On Your computer (not ieng6) create the file ~/.ssh/config:
Host <shortcut> <possibly more shortcuts>
HostName <the host name of the ssh server>
User <your username on the ssh server>
Part 2: GDB Debugging
New GDB commands
start [ARGUMENTS]
Starts the program with the specified arguments and pauses at the first line of main.
break LINE_NUMBER
Sets a breakpoint at the specified line number. (Breakpoint: a line in the program at which GDB will stop at before the line executes.)
next
Executes to the next line of code.
step
If the next line contains a function call, steps into the first line of the function. Otherwise, behaves the same way as next.
continue
Continues running the program until the next breakpoint.
--

The line that is shown above the (gdb) prompt has not run yet. It is the line that will run if you type next.
Activity
(clone the github classroom repo from here: https://classroom.github.com/a/iSlIHwXP)
Part 3: Hacking
3.1. Background
Imagine that you're a less ethical student than I'm sure you actually are. You overhear from some other students in lab that there's a binary available on the pi-cluster that can show you your grades on assignments before we formally release them. You hear quieter whispers that someone found a way to use it to change their grade. Given our less-than-ethical assumption about your state of mind, you might be tempted to exploit this for yourself.
3.2. The Plot Thickens
You see some code open on the professor's laptop during office hours. You do
your best to commit it to memory and write it down (remember, you're acting
quite unethically in this story), because it strikes you that the code was
something regarding assignment scores.
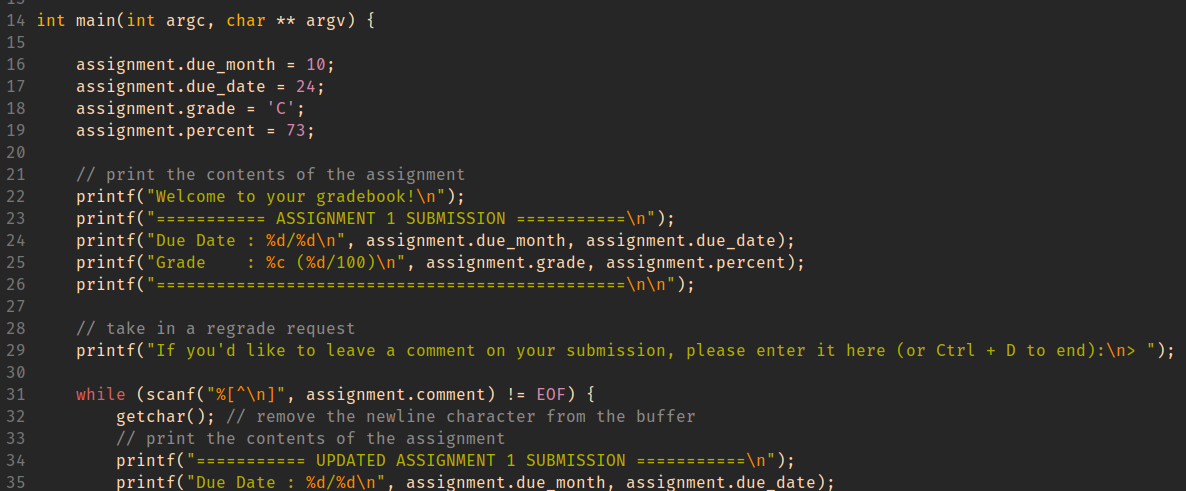
Using this information, you decide to give yourself and A with a score
to match while maintaining a real due date.
HINT
When important values are adjacent on the stack, overflowing an array with
values that you control can let you assign into other stack-allocated values.
GDB commands that may be useful for this activity:
-
(gdb) info locals -
(gdb) info args -
(gdb) print VALUE (or p VALUE)You can print any variable or expression, e.g. -
print x,p arr[5],p ((x & 0b1111) << 3) -
You can also specify a format to print in
-
print/t(binary),print/x(hex),print/d(decimal) -
(gdb) x ADDRESSThis prints out memory at an address, e.g. strings / arrays / pointers -
(gdb) x/16cb str1This prints the first 16 bytes ofstr1as characters -
(gdb) x/20xb str2This prints 20 bytes ofstr2in hex -
(gdb) x/4dw arrThis prints 4 "words" (i.e.int32s) ofarr, as decimal numbers -
You can use the following reference card for reference on gdb commands, and format commands for x and print.
Work Check-off
Push a copy-paste or screenshot of your gdb session from part 2 when investigating index_of_E to the github classroom assignment for this lab.